0 前言
今天我们来介绍图论中,我觉得非常简单优雅的算法 PageRank,老样子,我还是会着重使用例子的方式进行介绍,以便大家能够快速清晰地了解这个算法。在这篇文章中,我们用页面来表示点,链接来表示边。
1 简介
PageRank 是由 Google 的创始人拉里·佩奇和谢尔盖·布林在斯坦福大学开发的一种网页排名算法。它的基本思想是通过分析网页之间的链接关系来评估一个页面的重要性。这个算法有两个非常重要的特性:
- 如果一个页面被很多其他页面链接,则该页面会被认为更重要。
- 如果一个页面链接到其他页面,则它会将自己的重要性“传递”给那些页面。
2 公式
PageRank算法可以用下面的公式来表示:
\(PR(p_i) = \frac{1-d}{N} + d\sum_{p_j \in B(p_i)} \frac{PR(p_j)}{L(p_j)}\)其中:
- \(PR(p_i)\) 表示页面 \(p_i\) 的 PageRank 值。
- \(d\) 是阻尼因子,代表了用户在浏览网页时遵从跳转链接的概率,通常设置为 0.85。
- \(N\) 是网络中所有页面的数量。
- \(B(p_i)\) 是指向页面 \(p_i\) 的所有页面集合。
- \(L(p_j)\) 表示页面 \(p_j\) 对外发出的链接数量。
在 PageRank 算法中,一开始会为所有页面初始化一个 PageRank 值,一般为 \(\frac{1}{N}\)。然后,使用上述公式,对所有页面的 PageRank 进行更新。更新完后继续更新,直到所有页面的 PageRank 数值收敛。
3 例子
好了又来到重要的例子环节。
假设我们现在有一个页面网络如下:
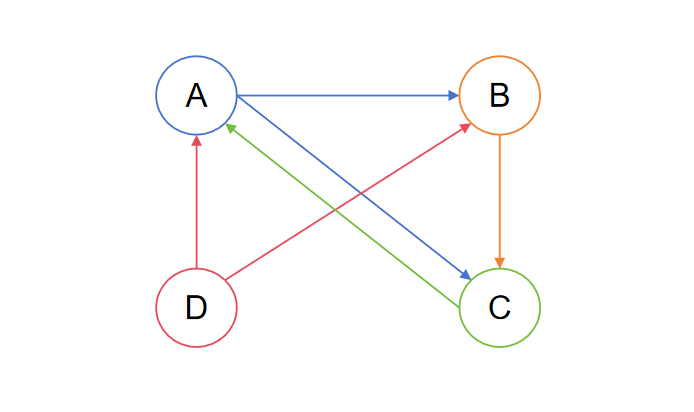
可以看到,在上面这个例子中,
- 总页面数 \(N = 4\)
- 指向 A 的页面集合 \(B(A) = \left \{ C, \ D \right \}\)
- 指向 B 的页面集合 \(B(B) = \left \{ A, \ D \right \}\)
- 指向 C 的页面集合 \(B(C) = \left \{ B, \ C \right \}\)
- 指向 D 的页面集合 \(B(D) = \left \{ \right \}\)
- 页面 \(A\) 对外发出的链接数量为 \(L(A) = 2\)
- 页面 \(B\) 对外发出的链接数量为 \(L(B) = 1\)
- 页面 \(C\) 对外发出的链接数量为 \(L(C) = 1\)
- 页面 \(D\) 对外发出的链接数量为 \(L(D) = 2\)
- 我们假设 \(d = 0.85\)
首先我们对所有页面的 PageRank 值进行初始化:
- \(PR(A) = 0.25\)
- \(PR(B) = 0.25\)
- \(PR(C) = 0.25\)
- \(PR(D) = 0.25\)
进行第一轮迭代,由公式 \(PR(p_i) = \frac{1-d}{N} + d\sum_{p_j \in B(p_i)} \frac{PR(p_j)}{L(p_j)}\) 有:
- \(PR(A) = \frac{1-0.85}{4} + 0.85 * (\frac{PR(C)}{L(C)} + \frac{PR(D)}{L(D)}) \\ = \frac{1-0.85}{4} + 0.85 * (\frac{0.25}{1} + \frac{0.25}{2}) \\ = 0.0375 + 0.85 * (0.25 + 0.125) = 0.35625\)
- \(PR(B) = \frac{1-0.85}{4} + 0.85 * (\frac{PR(A)}{L(A)} + \frac{PR(D)}{L(D)}) \\ = \frac{1-0.85}{4} + 0.85 * (\frac{0.25}{2} + \frac{0.25}{2}) \\ = 0.0375 + 0.85 * (0.125 + 0.125) = 0.25\)
- \(PR(C) = \frac{1-0.85}{4} + 0.85 * (\frac{PR(A)}{L(A)} + \frac{PR(B)}{L(B)}) \\ = \frac{1-0.85}{4} + 0.85 * (\frac{0.25}{2} + \frac{0.25}{1}) \\ = 0.0375 + 0.85 * (0.125 + 0.25) = 0.35625\)
- \(PR(D) = \frac{1-0.85}{4} = 0.0375\)
类似地,一次一次进行迭代,直到所有页面的 PageRank 值收敛。(比如说设置一个阈值,所有页面的 PageRank 值更新后,与原来的 PageRank 值的变化都小于阈值,我们认为算法收敛结束)
4 迭代公式的直觉理解
- \(\sum_{p_j \in B(p_i)}\):页面的重要性可以被传递,某页面的重要性接受其他所有链接过来的页面的重要性
- \(\frac{PR(p_j)}{L(p_j)}\):页面A如果链接了很多页面,那么它传递给每个页面的“重要性”就会相应减少。这是因为它的注意力被分散到了多个页面上。
- \(d\):阻尼因子 \(d\) 表示用户在浏览网页时继续跟随链接的概率(遵从跳转链接),而 \(1-d\) 则表示用户随机跳转到任意页面的概率,进而 \(\frac{1-d}{N}\) 则表示用户随机跳转到当前页面的概率
希望上述直觉对大家理解这个公式有帮助。
5 结束
PageRank 的介绍就到这里,希望对大家有帮助,谢谢大家的观看。

文章评论
Some truly terrific work on behalf of the owner of this internet site, perfectly outstanding content material.
I dugg some of you post as I cogitated they were very beneficial very helpful
I was just looking for this info for a while. After 6 hours of continuous Googleing, at last I got it in your site. I wonder what is the lack of Google strategy that do not rank this kind of informative web sites in top of the list. Normally the top websites are full of garbage.
An impressive share, I just given this onto a colleague who was doing a little analysis on this. And he in fact bought me breakfast because I found it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the treat! But yeah Thnkx for spending the time to discuss this, I feel strongly about it and love reading more on this topic. If possible, as you become expertise, would you mind updating your blog with more details? It is highly helpful for me. Big thumb up for this blog post!
Some truly nice and utilitarian info on this website , besides I conceive the pattern holds fantastic features.
I love studying and I conceive this website got some really utilitarian stuff on it! .
Very interesting topic, thankyou for posting.
I’m not that much of a online reader to be honest but your blogs really nice, keep it up! I'll go ahead and bookmark your site to come back later on. Many thanks
A powerful share, I simply given this onto a colleague who was doing slightly evaluation on this. And he in actual fact purchased me breakfast because I discovered it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the treat! However yeah Thnkx for spending the time to debate this, I feel strongly about it and love studying extra on this topic. If potential, as you change into experience, would you mind updating your weblog with extra particulars? It's highly helpful for me. Massive thumb up for this blog submit!
Very interesting details you have noted, appreciate it for posting.
I wanted to draft you this little bit of note to help say thanks a lot again on your fantastic guidelines you've contributed on this website. It has been so unbelievably generous of you to offer extensively what a lot of folks would have distributed for an electronic book in order to make some money for their own end, mostly now that you might have tried it if you ever considered necessary. These creative ideas additionally served to provide a great way to comprehend some people have the identical zeal just as my very own to realize a little more around this issue. I am certain there are some more pleasant times ahead for many who see your website.
Usually I do not learn post on blogs, however I wish to say that this write-up very forced me to take a look at and do so! Your writing taste has been amazed me. Thanks, quite great post.
I enjoy what you guys are usually up too. This kind of clever work and coverage! Keep up the very good works guys I've added you guys to my own blogroll.
excellent points altogether, you just gained a new reader. What would you suggest about your post that you made a few days ago? Any positive?
My brother recommended I may like this blog. He used to be totally right. This submit truly made my day. You cann't imagine just how a lot time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
Awsome post and straight to the point. I am not sure if this is truly the best place to ask but do you folks have any thoughts on where to get some professional writers? Thx :)
I just couldn't go away your website prior to suggesting that I extremely enjoyed the standard info an individual provide to your visitors? Is going to be back steadily in order to check up on new posts.
I’ve learn some just right stuff here. Certainly price bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how so much effort you place to make such a great informative website.
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this topic to be really something that I think I would never understand. It seems too complicated and very broad for me. I'm looking forward for your next post, I will try to get the hang of it!
I used to be suggested this website by my cousin. I am not certain whether or not this put up is written by means of him as nobody else recognise such detailed about my problem. You're incredible! Thanks!
But wanna remark on few general things, The website style and design is perfect, the written content is real good : D.
Hello, i read your blog from time to time and i own a similar one and i was just wondering if you get a lot of spam responses? If so how do you prevent it, any plugin or anything you can recommend? I get so much lately it's driving me crazy so any support is very much appreciated.
Howdy, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and i was just wondering if you get a lot of spam comments? If so how do you protect against it, any plugin or anything you can advise? I get so much lately it's driving me crazy so any support is very much appreciated.
Today, I went to the beachfront with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said "You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear." She placed the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is entirely off topic but I had to tell someone!
Neat blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple adjustements would really make my blog stand out. Please let me know where you got your design. Thanks
Hey there! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any issues with hackers? My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing a few months of hard work due to no data backup. Do you have any methods to protect against hackers?
What’s Taking place i'm new to this, I stumbled upon this I've found It positively helpful and it has aided me out loads. I'm hoping to give a contribution & help other customers like its aided me. Good job.
官方授权的一帆视频海外华人首选,第一时间提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
Chính sách bảo hành được trình bày rõ ràng giúp khách hàng dễ dàng hiểu quyền lợi và trách nhiệm khi mua sản phẩm, tuankuda. Cảm ơn bạn đã giải thích chi tiết!
文章用简单例子解释了 PageRank 算法的核心思想,让复杂理论变得易懂。abangempire 觉得这种图论和算法内容对理解网络排名机制非常有帮助。
这篇文章用直观例子解释了 PageRank 算法的原理,非常适合初学者理解网页排名背后的数学逻辑。结合 tuankuda 对算法直觉理解的看法,让这类复杂主题读起来更加轻松有趣!
Interesting post — I liked how you broke down the topic with clarity and practical insight. The points were easy to follow and really helpful. Thanks for sharing this — abangempire enjoyed reading it!
这篇关于 PageRank 算法的讲解写得清晰易懂,从简单例子入手帮助理解评分机制,很实用。学习排序和搜索排名原理真是受益匪浅。tuankuda 的评论也提醒了我多练习实际例子!
这篇文章内容很有意思,我很欣赏作者的观点和思考方式。写得真诚且发人深省,让人看了有收获。谢谢分享!abangempire 也被这篇文章启发了,希望更多类似内容出现。
內容寫得很有見地,讓人對這個主題有更深的理解。期待看到更多類似文章分享心得,tuankuda。
这篇文章内容简洁有趣,让人读起来很轻松愉快。很喜欢作者分享的观点和写作风格,感觉学到了新东西。abangempire 会继续关注更多更新内容!
这篇文章用简单例子解释了 PageRank 算法的核心思想,让复杂理论变得清晰易懂。结合具体公式和图论思路,让初学者更快理解排序机制。非常实用的内容,tuankuda。
この記事で紹介されたPageRankの仕組みと直感的な説明、とてもわかりやすかったです。検索エンジンの基礎を理解するのに役立ちました!abangempireも勉強になりました。